ANALCHEM SPE Technology
Solid Phase Extraction Technology utilizes the principle of selective retention of analytes that characterizes the powerful separation technique of HPLC. It is a physical extraction process that involves a liquid phase and a solid phase. The solid support (chemically modified silica surface/sorbent) has a greater attraction for the isolate (analyte) than the solvent in which the isolate is dissolved.
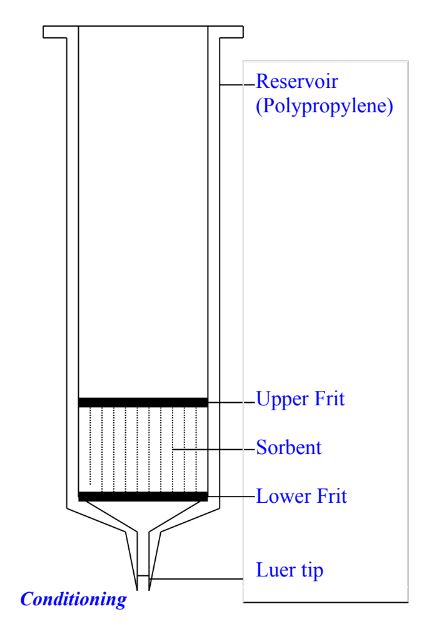
By choosing a proper solid support, packed in a polypropylene tube with open barrel configuration as shown in the figure, very selective extraction of high purity isolate can be achieved.
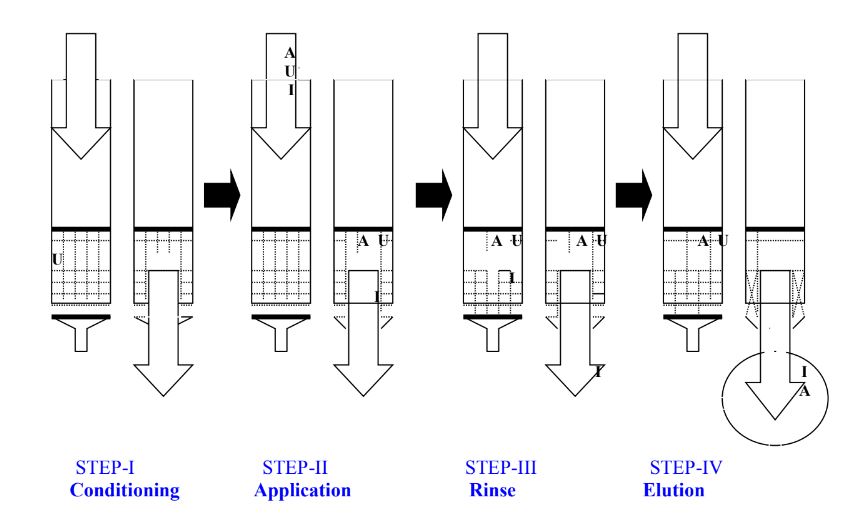
There are four steps involved in the SPE process:
STEP-I : Conditioning
STEP-II : Application
STEP-III : Rinse
STEP-IV : Elution
STEP-I : Conditioning
Active sites of the support are not available to interact with analytes because the solid support is packed dry in a tube. Therefore, conditioning the packed columns prior to sample application, to open the active sites of the support, is a key process in SPE technology to ensure reproducible retention of the analytes.
STEP-II : Application (Retention)
The compounds of interest (analytes or isolates), dispersed in a matrix containing other impurities and undesired materials is applied on to the column at a slow flow rate. A slow rate of sample application is necessary to achieve maximum retention of the analytes.
A Analytes in matrix
I Other matrix impurities
U Undesired matrix constituents
STEP-III : Rinse
The column is rinsed with a specific solvent or combination of solvents to remove matrix impurities (I).
STEP-IV : Elution
Selective elution of pure analytes (A) is achieved by using specific solvents, some of the undesired matrix constituents (U) are left behind on the support.
SAMPLE PREPARATION: FLOW DIAGRAM